Red Mountain targets early cashflow with kaolin project acquisition

Pic: Tyler Stableford / Stone via Getty Images
Special Report: Red Mountain Mining is taking the plunge into the high purity alumina space with the acquisition of a previously producing kaolin project in WA.
High purity alumina for (HPA) is one of the rising stars of the resources sector — small wonder given its emerging use in things like LED lights and lithium-ion batteries.
Red Mountain Mining (ASX:RMX) is now grabbing a piece of the kaolin pie with its binding agreement to acquire the historic 84sqkm Mt Kokeby project, about 99km southeast of Perth.
Red Mountain says old drilling hit high-grade kaolin with more than 30 per cent alumina content, making the project a potential candidate for a low capex, direct shipping ore (DSO) operation for early cashflow.
This is supported by the project’s close proximity to rail and all-weather roads that provide access to container handling at Fremantle port and bulk handling at Kwinana.
Mt Kokeby also has exploration upside, Red Mountain says, as significant areas of the Murray deposit remain untested.
The company has also restructured its agreement to acquire the Mt Mansbridge heavy rare earths project, just 40km from Northern Minerals’ (ASX:NTU) advanced Browns Range project.
Red Mountain now has an exclusive 28-day due diligence period following which it can earn 100 per cent of both the Mt Kokeby and Mt Mansbridge projects for $500,000 in cash and 310 million shares.
“The introduction of two high-quality specialty metal Western Australian projects is an exciting development for the company,” Red Mountain director Jeremy King said.
“Our view is that both the HPA and rare earths markets are attractive places for a producer to be, and with each project at different stages they complement each other well.”
Kaolin: an emerging market
Research firm Markets and Markets has forecast the kaolin market to grow at a compound annual growth rateof 4.1 per cent to reach $US5.52 billion by 2022.
It is used in the paper industry, as a coating material to strengthen fibreglass, and in the paint and ceramics industry as a substitute for titanium dioxide.
However, it is its use as feedstock for the HPA industry that could well drive demand growth for kaolin.
Current demand for HPA is dominated by the production of synthetic sapphire to manufacture of LED lights.
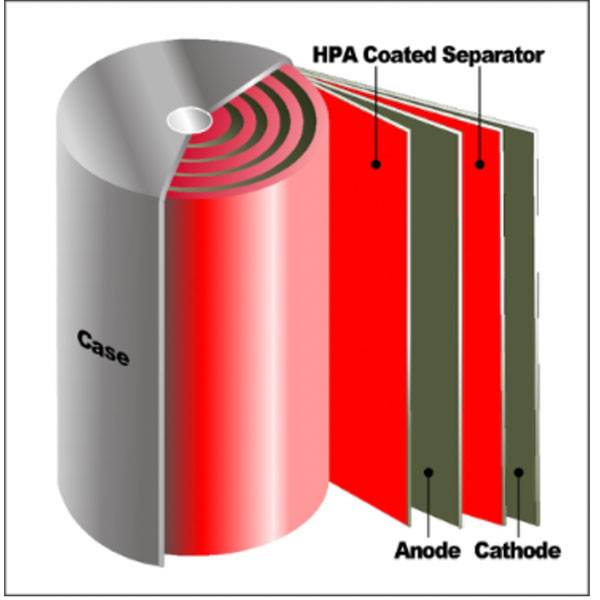
Its heat resistive properties also make it ideally suited for coating the separators that keep apart the cathode and anode electrodes in lithium-ion batteries — increasing safety and stability while allowing for higher energy density in a more compact design.
READ MORE: Red Mountain set to break into the lucrative heavy rare earths market
This story was developed in collaboration with Red Mountain Mining, a Stockhead advertiser at the time of publishing.
This story does not constitute financial product advice. You should consider obtaining independent advice before making any financial decisions.
UNLOCK INSIGHTS
Discover the untold stories of emerging ASX stocks.
Daily news and expert analysis, it's free to subscribe.
By proceeding, you confirm you understand that we handle personal information in accordance with our Privacy Policy.