Strategic Elements eyes US$10B electric skin patch market for its moisture-based battery tech
The electric skin patch market is forecast to grow to US$27 billion by 2033. Pic via Getty Images
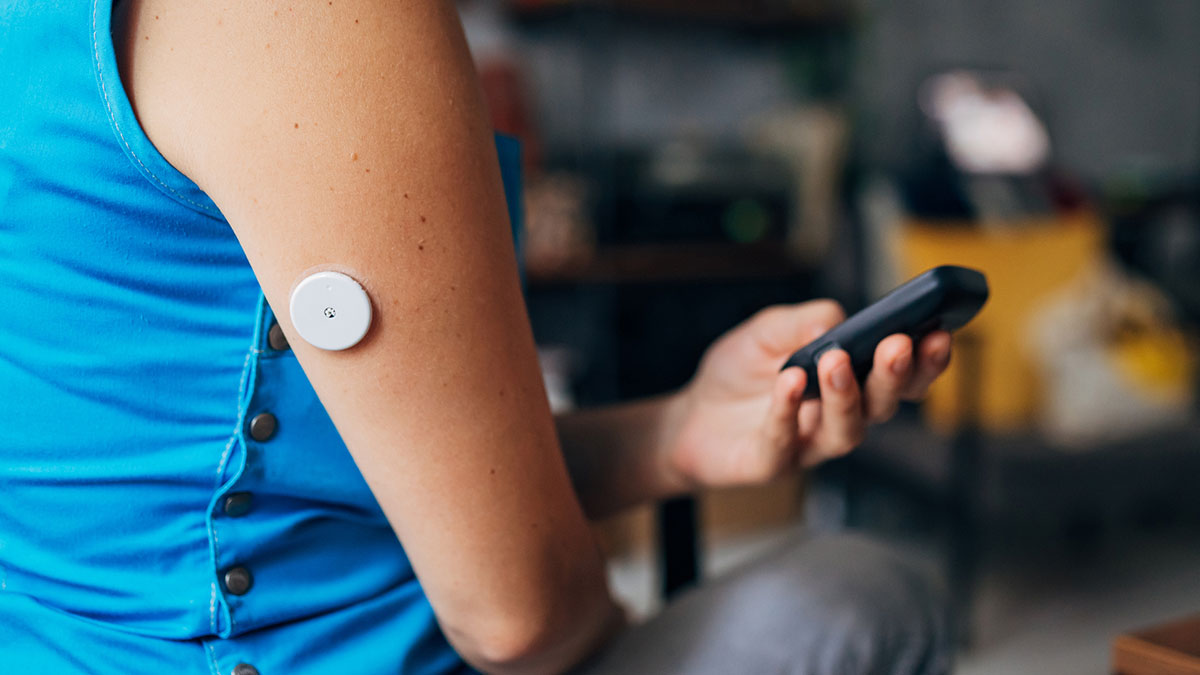
Strategic Elements has successfully demonstrated the power output of its Energy Ink battery, which generates electrical energy from moisture in the air, compared to the baseline power consumed by a glucose monitoring skin patch.
The extremely thin, flexible, environmentally friendly Energy Ink battery generated over 200% more power than required.
Strategic Elements (ASX:SOR) MD Charles Murphy says the technology is evolving at a rapid rate.
“It was a fantastic result to clearly produce more than enough power compared to a leading existing glucose monitoring patch being used by millions of people worldwide and to have the excess potential for a manufacturer to include more advanced sensing or other features,” he said.
“The thinness, flexibility, printability, safety, and environmentally friendly aspects of the technology are all very attractive, however, it needs to produce enough power to be truly commercially useful.
“Hence, we are extremely pleased with the trajectory of the Energy Ink development.”
Skin patches a US$10B market
Not to mention, electronic skin patches are currently a large US$10 billion market, forecast to grow to US$27 billion by 2033.
Millions of people worldwide use skin patches powered by rigid alkaline batteries or lithium materials to reduce the frequency of daily finger prick blood glucose checks and better manage glucose levels.
However, the ACC is concerned with child safety of the button/coin cell batteries used in these types of devices and in 2022 ordered manufacturers/retailers to comply with strict new Australian mandatory safety and information standards.
“With the use of these devices expected to surge globally, the clear goal for manufacturers is to make devices as inconspicuous as possible, provide more advanced sensing, keep costs low, and be friendlier to the environment,” SOR says.
“The advantages of the Energy Ink technology align with these goals and include flexibility, thinness, and the ability to print various sizes whilst using environmentally friendly materials.”
More power per square centimetre
The successful design and fabrication of programmable load simulators proved to increase the data available to the engineering team, speed up testing, and drive optimisation of the technology.
Plus, a simple power management system was combined with Energy Ink technology for the first time – and initial testing revealed an over 500% increase in power density or power per square centimetre.
Murphy says the power management systems have the potential to dramatically increase the performance of an Energy Ink power solution.
“The sudden escalation in power per square centimetre from a rudimentary, very simple power management system has provided the team with great optimism for Q1, 2023 and what could potentially be achieved through this approach,” Murphy says.
Large scale Energy Ink systems
Notably, because the Energy Ink technology is still in early development, the fundamental upper limit of aspects such as maximum power output, duration and energy density remains unknown.
Printed graphene-oxide-based cells that generate energy from airborne water molecules have the potential to directly power a device, complement a battery by extending device life or provide energy for battery storage.
The global imperative for more innovative, renewable energy creation and power sources is expected to grow significantly.
The company is also confident of a potential R&D pathway for larger-scale Energy Ink systems either through packs with multiple connected cells or larger cell sizes.
SOR is currently designing a program of work that will significantly increase the cell size under development, with further information on the program is expected in Q1, 2023.
This article was developed in collaboration with Strategic Elements Limited, a Stockhead advertiser at the time of publishing.
This article does not constitute financial product advice. You should consider obtaining independent advice before making any financial decisions.
Related Topics
UNLOCK INSIGHTS
Discover the untold stories of emerging ASX stocks.
Daily news and expert analysis, it's free to subscribe.
By proceeding, you confirm you understand that we handle personal information in accordance with our Privacy Policy.








