Puzzle pieces fall into place at GreenTech’s Pilbara lithium project with 700m Osborne pegmatite strike

GreenTech Metals has various work programs planned across its Pilbara lithium projects in 2024 to build on its understanding of known pegmatite trends. Pic via Getty Images
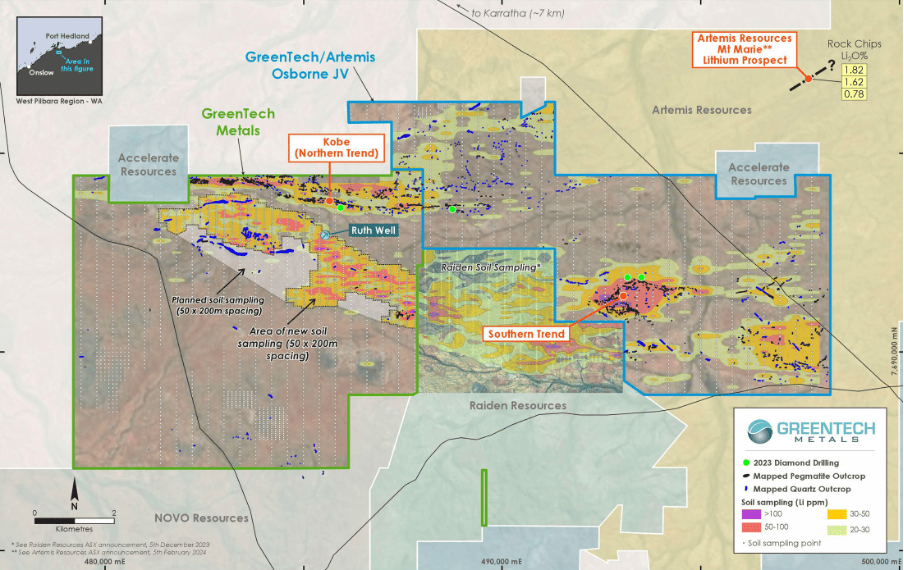
- 2023 drilling has provided new information of the Southern Trend pegmatites at GreenTech’s Pilbara lithium projects
- The Osborne pegmatite in particular is evolving into a key priority with some 700m of strike
- A maiden RC drilling program is planned for March 2024 to test near-surface lithium at the Osborne pegmatite where ground access has now been granted
Special Report: A recently completed diamond drill program has provided new information on the Osborne pegmatite trend which is evolving into a very exciting target with some 700m of strike.
GreenTech Metals (ASX:GRE) carried out a four-hole diamond drilling program totalling 1,600m in late 2023, with two holes drilled on the Kobe pegmatite trend and another two on the Southern pegmatite trend.
Southern Trend
Numerous pegmatites with variable thicknesses up to 24.6m were intersected in the Southern trend drilling, however, these were found to not reflect the thicknesses of the surface pegmatite outcrop, or the high lithium grades of the Osborne pegmatite at surface.
Drilling confirmed thick pegmatites are present as part of the Southern trend pegmatites, and are also lithium-fertile based on the presence of pathfinder elements such as tantalum and niobium.
Kobe Trend
The drilling at Kobe intersected spodumene bearing pegmatites. This confirmed the fertility of the Kobe trend at depth and is consistent with the persistence of lithium mineralisation seen along the full 7.5km strike of Kobe.
New extensions to lithium prospects
Meanwhile, geological mapping and infill rock chip sampling has confirmed the continuity of pegmatite-hosted lithium mineralisation in the Northern (Kobe target) trend as well as identifying a new high-grade Li2O extension to the Osborne trend.
Standout results from this program include:
- 2.36% Li2O, 32ppm tantalum, and 92ppm niobium;
- 1.98% Li2O, 23ppm tantalum, and 62ppm niobium; and
- 1.64% Li2O, 3ppm tantalum, and 14ppm niobium.
These results extend the Osborne mineralisation 600m further west for a total strike length of 700m and remains open.
Various work programs ahead
“We have seen our understanding of the Osborne pegmatite trend evolve into a very exciting target with some 700m of strike and with high lithium grades at surface and with the potential for thicker intersections of pegmatite at depth,” GRE executive director Tom Reddicliffe says.
“Kobe remains a very prospective target due to the 7.5km of strike length and the persistence of the high lithium grades at surface that persist along the entire strike.
“Going forward we will be looking at ways to identify wider pegmatite zones at Kobe which may be present at depth.
“Our forward programs including a maiden RC drill program that will begin at Osborne and which will aim to build on our understanding of known pegmatite trends, as well as identifying new zones that have been highlighted by our rock chip sampling and soil sampling.”
What’s next?
Based on this new information and the additional rock chip sampling results, GRE says the Osborne pegmatite remains a priority target for drill testing.
Mapping and rock chip sampling, along with a program of infill soil sampling to test the Southern trend within the Ruth Well tenements beneath shallow cover, are also planned for this quarter.
GRE is continuing to research and review historic datasets with a view towards potentially identifying new lithium pegmatite trends, as well as extensions to the known trends within the broader Ruth Well and Osborne project areas.
This article was developed in collaboration with GreenTech Metals, a Stockhead advertiser at the time of publishing.
This article does not constitute financial product advice. You should consider obtaining independent advice before making any financial decisions.
Related Topics

UNLOCK INSIGHTS
Discover the untold stories of emerging ASX stocks.
Daily news and expert analysis, it's free to subscribe.
By proceeding, you confirm you understand that we handle personal information in accordance with our Privacy Policy.








