These ASX battery companies are well-placed to meet stricter European regulations
Energy
Energy
Shares in battery company EcoGraf (ASX:EGR) have soared as it reached a milestone in its recycling process that recovers graphite anode material for re-use in lithium-ion batteries for EVs.
The company achieved ‘outstanding’ results of 99.95 per cent carbon purity in testing for its proprietary recycling process that recovers carbon anode material from battery production waste.
EcoGraf said its recycling strategy is supported by European Union law changes which insist on manufacturers eliminating more waste in their battery production process.
The European Union has raised its targets for battery waste recovery to 65 per cent by 2025, and to a level of 70 per cent by 2030.
“The stricter regulations demonstrate Europe’s intention to improve sustainability across the lithium-ion battery life cycle and encourage EV and battery manufacturers to contribute towards a climate neutral economy through greater battery recycling,” said the company.
Meanwhile, in an important development for the EV sector, US carmaker General Motors has announced its plans to phase out production of diesel and petrol cars and trucks by 2035.
GM’s sudden shift comes only days after the inauguration of President Joe Biden who has pledged to boost sales of EVs, including purchases by the US government.
“General Motors is joining governments and companies around the globe working to establish a safer, greener and better world,” said GM chairman and chief executive, Mary Barra.
An EV’s battery represents more than 40 per cent of an electric vehicle’s total carbon emissions over its product lifespan.
Eliminating waste in the battery production process can therefore contribute to a reduction in battery costs and carbon emissions.
EcoGraf is moving ahead with its pilot recycling plant for carbon anode material and is working with several EV companies and battery manufacturers on the project.
The company’s proprietary recycling process for lithium-ion batteries does not use any hydrofluoric acid.
In addition to its recycling project, EcoGraf is building a state-of-the-art facility in WA to manufacture spherical graphite products for export markets in Asia, America and Europe.
EcoGraf is developing its TanzGraphite natural flake graphite business in Tanzania for which sales agreements have been negotiated with Germany’s ThyssenKrupp and Japan’s Sojitz.
The Epanko graphite project is located 370km west of Dar es Salaam in Tanzania and has a production capacity of 60,000 tonnes per year over an 18-year mine life.
Another ASX battery sector company, Talga Group (ASX:TLG) also noted the tighter regulatory environment in the European Union for battery anode manufacturers from which it is positioned to benefit.
“In Europe, the moves to introduce a battery materials ‘passport’ requiring stricter emissions regulations on imported battery materials, and growing financial and regulatory support for local manufacturers supports Talga’s plans,” said managing director, Mark Thompson.
“We are also glad to see the increased realisation of these factors in capital markets, with newly economic, social and governance funds rotating out of fossil fuel investments towards sustainable transport and battery materials,” said Thompson.
Talga Group is developing an integrated battery anode production plant in Sweden for anode products and lithium-ion batteries.
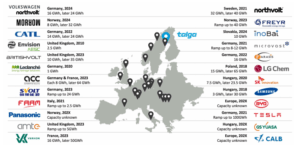
The company said 24 battery megafactories are planned for Europe over the coming years and include facilities operated by Tesla, Volkswagen and Panasonic.
The two dozen plants will have a combined production capacity for battery anode of 600,000 to 700,000 tonnes per year, enough to equip 9 million to 10 million EVs per year.
Another ASX company is aiming to produce green lithium-ion battery cells for the storage of renewable energy and for the electrification of transport technologies.
Magnis Energy Technologies (ASX:MNS) is working with the University of Newcastle to deploy a big battery into Fletcher International Exports’ processing plant in Dubbo, NSW.
The company has also entered into agreements with the University of Newcastle, Binghamton University and through its C4V technology partner with the US Department of Energy.
C4V is providing lithium-ion battery technology for the US Department of Energy project into grid stabilisation for solar powered generation.
The company is involved in projects for lithium-ion battery cell gigafactories that are currently planned for development in New York and Townsville in Australia.
At Stockhead we tell it like it is. While Talga Group is a Stockhead advertiser, it did not sponsor this article.